A machine learning algorithm to detect pine wilt disease using UAV-based hyperspectral imagery and LiDAR data at the tree level
Pine wilt disease (PWD) is caused by the pine wood nematode (PWN, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) and is spread through the insect vector pine sawyer beetle (Monochamus spp.). It is a global destructive threat to forests, having caused extreme damage in China. Currently, PWD management countermeasures are mostly based on the control of dead trees after the onset of an outbreak by fumigation, burning, and tree-felling operations. Therefore, the development of a more effective method to monitor and control the spread of PWD is imperative. Remote sensing is considered a potential approach to detect forest pest and diseases. However, certain limitations exist in the detection of forest disturbance by ground and satellite remote sensing. Conversely, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) remote sensing is efficient and flexible, and the device can be equipped with high-resolution remote sensing sensors. In addition, LiDAR can accurately collect three-dimensional information of objects and the potential of LiDAR for forest health monitoring has been considerably augmented. Specifically, when we used hyperspectral imaging (HI) data alone, it was difficult to precisely segment tree crowns, and the shadow and overlaps of tree crowns caused spectral confusion. LiDAR can overcome these problems by obtaining the structural features of trees; the variables derived from LiDAR data can also be used for the detection of forest pest. However, a combination of HI and LiDAR has not been applied in monitoring PWD.
Based on this, in the attached article “A machine learning algorithm to detect pine wilt disease using UAV-based hyperspectral imagery and LiDAR data at the tree level”, scientists from Beijing Forestry University conducted field experiments in the northeastern area of Yiwu City (29°24′45′′ -29°25′59′′ N, 120°09′40′′ -120°10′38′′ E), Zhejiang Province of China in October 2020. The objectives of this study were to (1) examine the most sensitive spectral variables and LiDAR metrics for detecting the tree infection stages of PWD; (2) compare the capabilities of HI and LiDAR data for predicting the infection stages of PWD and (3) explore the potential of the combination of HI and LiDAR datasets for an improvement in the accuracy.
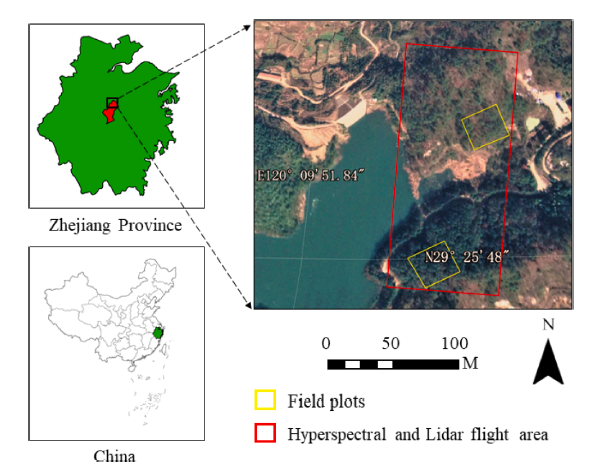
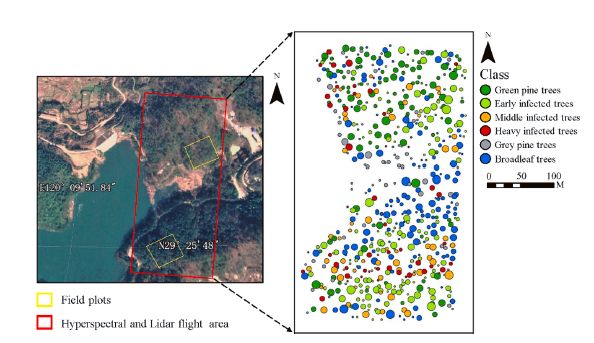
Locations of the study and UAV flight areas. The yellow rectangles represent two sampled plot locations, and the red rectangle represents hyperspectral and LiDAR flight area.
The authors combined needle, ground tree, and UAV images to classify the PWD infection into five stages and defined the infection stages by resin secretion, growth vigor, and color of the needles.
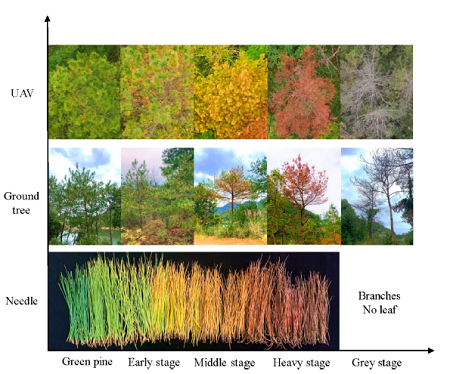
Images of needles, ground trees, and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images of pine trees at different PWD infection stages.
HI data was collected employing the Pika L hyperspectral camera (Resonon, USA) and DJI Matrice 600 UAV (DJI, Shenzhen, China). LiDAR data were acquired at the same time, using the LR1601-IRIS UAV-mounted system (IRIS Inc., China, LICA United Technology Limited).
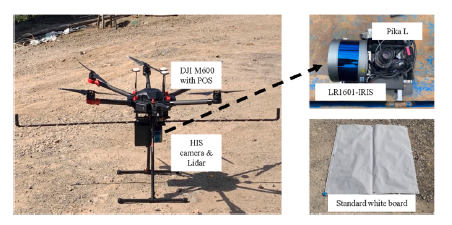
The UAV-based system with LR1601-IRIS LiDAR and Pika L imaging spectrometer.
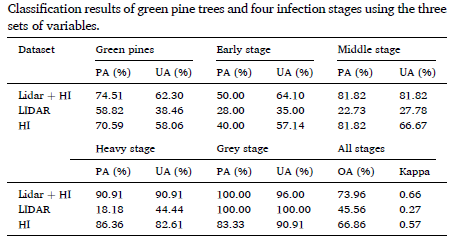
The authors obtained the following results: (1) The classification accuracies of HI (OA: 66.86%, Kappa: 0.57) were higher than those of LiDAR (OA: 45.56%, Kappa: 0.27) for predicting PWD infection stages, and their combination had the best accuracies (OA: 73.96%, Kappa: 0.66); (2) LiDAR data had higher ability for dead tree identification than HI data; and (3) The combined use of HI and LiDAR data for estimation of PWD infection stages showed that LiDAR metrics (e.g., crown volume) were essential in the classification model, although the variables derived from HI data contributed more than those extracted from LiDAR.
Comparison of different PWD infection stages of ten variables based on hyperspectral and LiDAR features.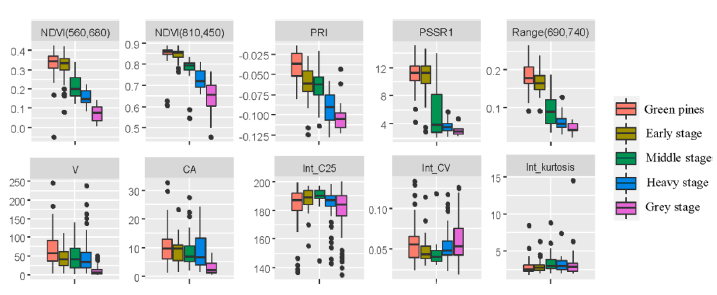
Tree crown PWD infection stage mapping combining the HI and LiDAR data in the UAV flight area.
In this paper, the authors examined the potential for estimating the tree stage of PWD infection applying airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data (uncalibrated) at the tree level. They found that a combination of HI and LiDAR datasets increased the accuracy of the classification of five stages from 66.86% (only HI) and 45.56% (only LIDAR) to 73.96%. The presented LiDAR variables (crown volume and crown area) are essential to the implementation of this novel classification model. The UAV-based system combining hyperspectral and LiDAR sensors possesses powerful potential for early-stage PWD detection to prevent PWD spread before an outbreak has occurred. They expect that the accuracy established here can be further improved by using a new algorithm and a calibrated SWIR.
 6376420843668349672798517.pdf
6376420843668349672798517.pdf